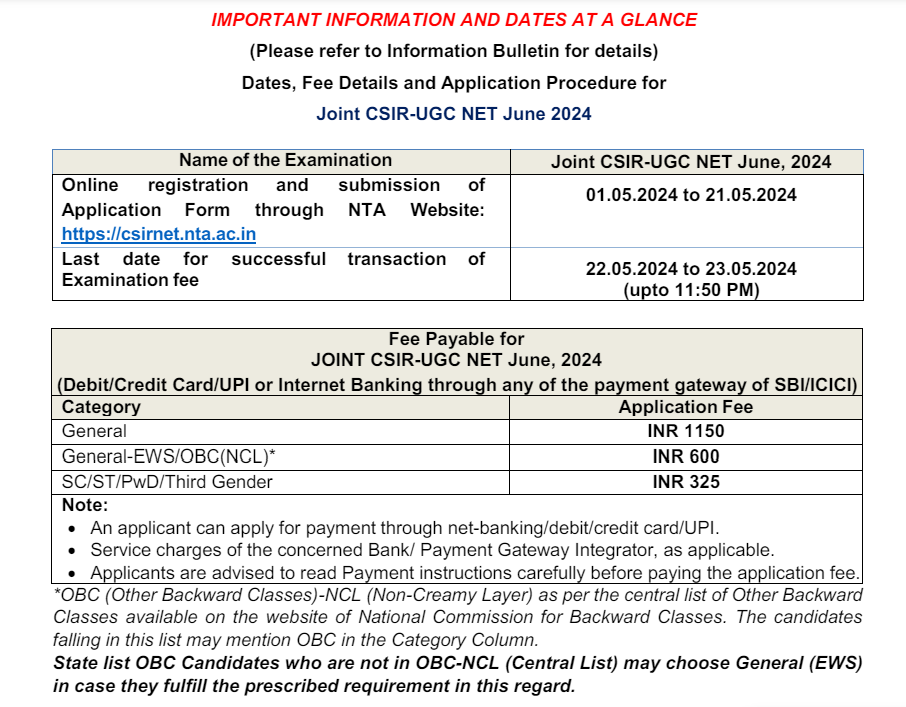
Fluid Mechanics 2 And 3

Category –ME Online Test
Telegram-Join Us On Telegram
Attempt Free Fluid Mechanics 2 And 3 Here. Read The Important Electrical MCQ From Below.
1) Shear stress in static fluid is
a. always zero
b. always maximum
c. between zero to maximum
d. unpredictable
ANSWER: always zero
2) Which branch of fluid mechanics deals with translation, rotation and deformation of the fluid element without considering the force and energy causing such motion is called as
a. fluid dynamics
b. fluid kinematics
c. fluid kinetics
d. hydraulics
ANSWER: fluid kinematics
Fluid Mechanics 2 And 3
3) Inter molecular cohesive force in the fluids is
a. less than that of the solids
b. more than that of the solids
c. equal to that of the solids
d. unpredictable
ANSWER: less than that of the solids
4) The specific weight of the fluid depends upon
a. gravitational acceleration
b. mass density of the fluid
c. both a. and b.
d. none of the above
ANSWER: both a. and b.
5) Which property of the fluid offers resistance to deformation under the action of shear force?
a. density
b. viscosity
c. permeability
d. specific gravity
ANSWER: viscosity
6) In which method of describing fluid motion, the observer remains stationary and observes changes in the fluid parameters at a particular point only?
a. Lagrangian method
b. Eulerian method
c. Stationary method
d. All of the above
ANSWER: Eulerian method
Fluid Mechanics 2 And 3
7) The rate of increase of velocity with respect to change in the position of fluid particle in a flow field is called as
a. local acceleration
b. temporal acceleration
c. convective acceleration
d. all of the above
ANSWER: convective acceleration
8) The actual path followed by a fluid particle as it moves during a period of time, is called as
a. path line
b. streak line
c. filament line
d. stream line
ANSWER: path line
9) The imaginary line drawn in the fluid in such a way that the tangent to any point gives the direction of motion at the point, is called as
a. path line
b. streak line
c. filament line
d. stream line
ANSWER: stream line
Fluid Mechanics 2 And 3
10) Which type of fluid flow is shown in below diagram?
a. Circular flow
b. Rotational flow
c. Irrotational flow
d. None of the above
ANSWER: Irrotational flow
11) The study of force which produces motion in a fluid is called as
a. fluid statics
b. fluid dynamics
c. fluid kinematics
d. none of the above
ANSWER: fluid dynamics
12) Which of the following forces generally act on fluid while considering fluid dynamics?
1. Viscous force
2. Pressure force
3. Gravity force
4. Turbulent force
5. Compressibility force
a. (1), (3), (4) and (5)
b. (1), (2), (3) and (5)
c. (1), (2), (3) and (4)
d. (1), (2), (3), (4) and (5)
ANSWER: (1), (2), (3), (4) and (5)
Fluid Mechanics 2 And 3
13) The net force of an ideal flow is equal to the sum of nonzero values of
a. pressure force and gravity force
b. viscous force and gravity force
c. pressure force and viscous force
d. pressure force, viscous force and compressibility force
ANSWER: pressure force and gravity force
14) When the net force acting on a fluid is the sum of only gravity force, pressure force and viscous force, the equation is called as
a. Reynold’s equation of motion
b. Navier-stockes equation of motion
c. Euler’s equation of motion
d. none of the above
ANSWER: Navier-stockes equation of motion
15) In a steady, ideal flow of an incompressible fluid, total energy at any point of the fluid is always constant. This theorem is known as
a. Euler’s theorem
b. Navier-stockes theorem
c. Reynold’s theorem
d. Bernoulli’s theorem
ANSWER: Bernoulli’s theorem
16) The flow of fluid will be laminar when,
a. Reynold’s number is less than 2000
b. the density of the fluid is low
c. both a. and b.
d. none of the above
ANSWER: both a. and b.
Fluid Mechanics 2 And 3
17) How should be the viscosity of the flowing fluid for laminar flow?
a. viscosity of the fluid should be as low as possible, for laminar flow
b. viscosity of the fluid should be as high as possible, for laminar flow
c. change in viscosity of the flowing fluid does not affect its flow
d. unpredictable
ANSWER: viscosity of the fluid should be as high as possible, for laminar flow
18) Below diagram shows the velocity distribution of fluid flow through a pipe. Flow is laminar.
What is the ratio of maximum velocity to average velocity?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 4
d. 3.14
ANSWER: 2
19) Coefficient of friction for laminar flow is given as
Where,
Re = Reynold’s number
a. (Re / 32)
b. (32 / Re)
c. (Re / 16)
d. (16 / Re)
ANSWER: (16 / Re)
Fluid Mechanics 2 And 3
20) What is the ratio of maximum velocity to average velocity, when the fluid is passing through two parallel plates and flow is laminar?
a. 3/2
b. 2/3
c. 4/3
d. 3/4
ANSWER: 3/4
21) The head loss through fluid flowing pipe due to friction is
a. the minor loss
b. the major loss
c. both a. and b.
d. none of the above
ANSWER: the major loss
22) What is Darcy-Weisbach formula for heat loss due to friction?
Where,
f = Darcy’s coefficient of friction
a. hf = (f l V2) / (g d)
b. hf = (f l V2) / (2 g d)
c. hf = (4 f l V2) / (2 g d)
d. hf = (16 f l V2) / (2 g d)
ANSWER: hf = (4 f l V2) / (2 g d)
Fluid Mechanics 2 And 3
23) Minor losses occur due to
a. sudden enlargement in pipe
b. sudden contraction in pipe
c. bends in pipe
d. all of the above
ANSWER: all of the above
24) Minor losses do not make any serious effect in
a. short pipes
b. long pipes
c. both the short as well as long pipes
d. cannot say
ANSWER: long pipes
25) What is the correct formula for loss at the exit of a pipe?
a. hL = 0.5 (V2 / 2g)
b. hL = (V2 / 2g)
c. hL = (2 V2 / g)
d. hL = (4 V2 / g)
ANSWER: hL = (V2 / 2g)
Fluid Mechanics 2 And 3