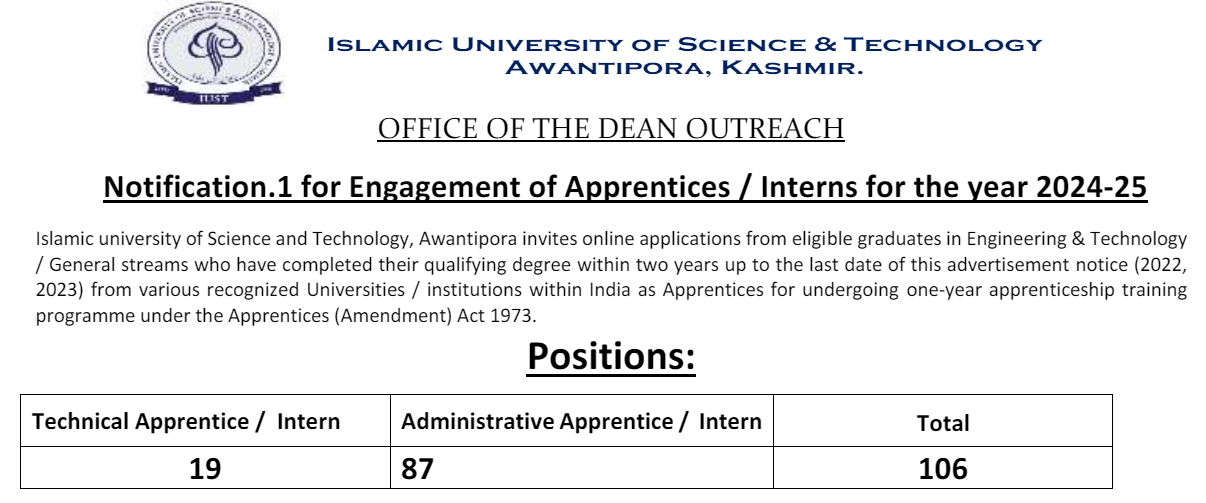
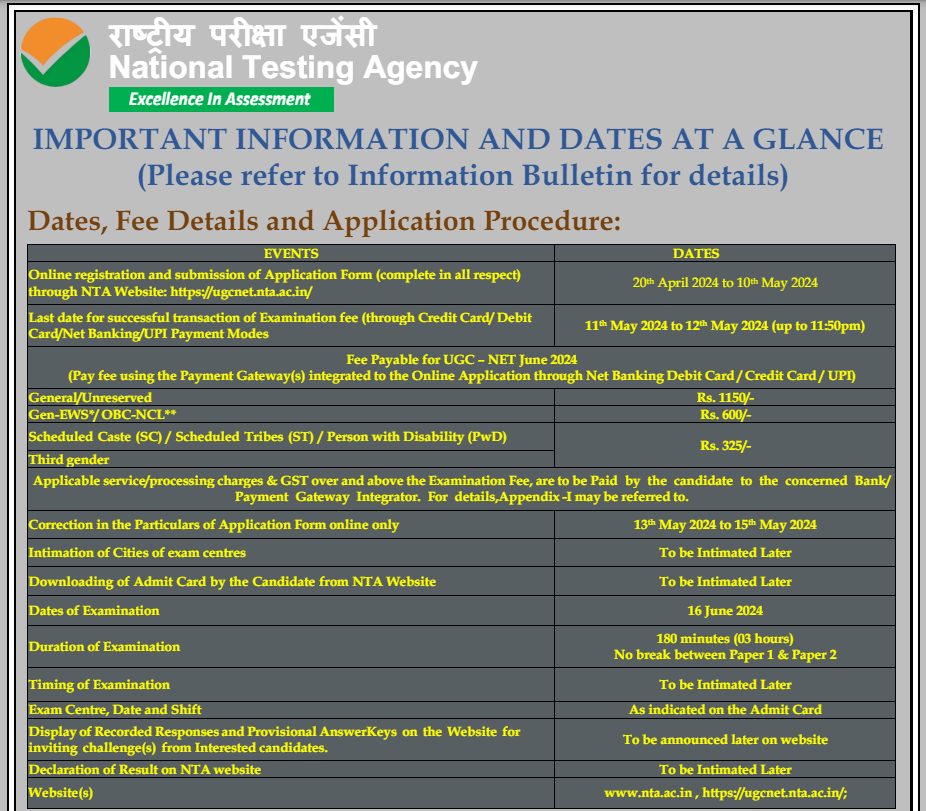
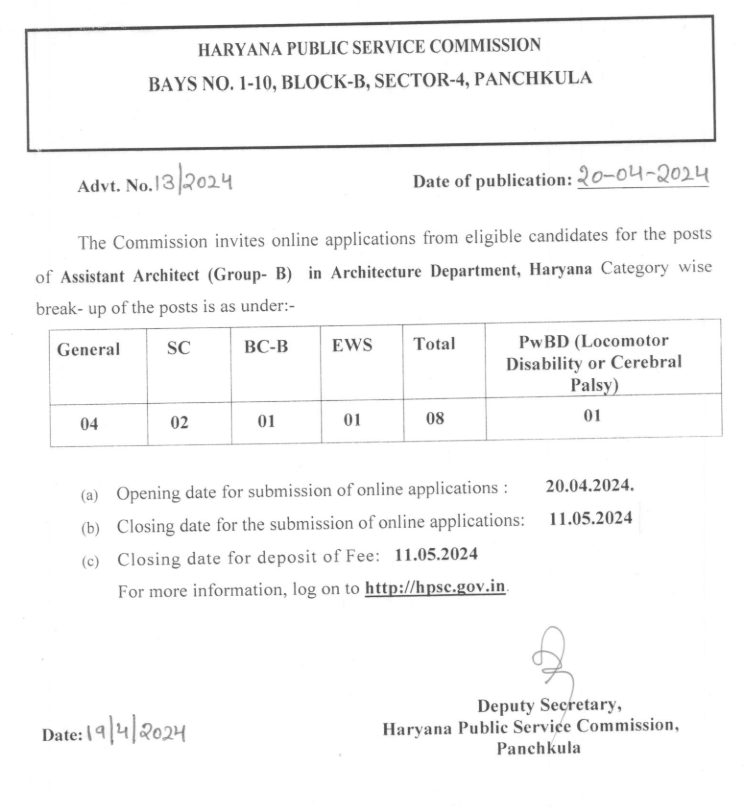
The
Voice-There
are two ways to express an action of a subject in relation to its object
•
Passive voice
In “active
voice” subject acts upon object, while in “passive voice” object is acted upon
by subject. It can also be said, in “active voice” subject does a work on
object, while in “passive voice” object is worked on by subject. The normal
structure of an active voice sentence is subject+verb+object but
in passive the normal structure of sentence is reversed according to certain
rules and becomes like object+verb+subject. The real meaning of a
sentence does not change if the sentence is expressed either by active voice or
by passive voice. The active voice is mostly used in writing because it
gives a direct and more concise meaning. Passive voice is used sometimes due to
the following reasons.
- When
intentionally hiding the subject of sentence. For example, a student who
failed in exam might say, some chapters were not studied.
Another example. Women were not treated as equals - When
passive voice better explain thought of sentence. For example, to say, cloth
is sold in yards, is more meaningful than to say, Shop keepers sell
cloth in yards. - When
passive voice better emphasizes the main though of the sentence. For
example, a man who is being teased by another person might say in anger, “you
will be beaten by me” - When
subject is not exactly known. For example, His watch was stolen. It
is not known that who stole his watch, the subject (thief) is not exactly
known so it is better to use passive voice for such sentence.There are
certain rules for expressing a thought in passive voice or for changing a
sentence from active voice to passive voice.
Fundamental
Rules for changing from active voice to passive voice
- The
places of subject and object are interchanged i.e. the object shifts to
the place of subject and subject shifts to the place of object in passive
voice. Example.
Active voice: I write a letter.
Passive voice: I letter is written by me.
Subject (I) of sentence shifted to the place of object (letter) and object
(letter) shifted to the place of subject (I) in passive voice. - Sometimes
subject of sentence is not used in passive voice. Subject of sentence can
be omitted in passive voice, if without subject it can give enough meaning
in passive voice.Examples.
Passive voice: cloth is sold in yards - 3rd
form of verb (past participle) is always used as main verb in
sentences of passive voice for all tenses. Base form of verb or present
participle will be never used in passive voice.
The word “by” is used before subject in sentences in passive voice.Example.
Active voice: He sings a song.
Passive voice: A song is sung by him. - The
word “by” is not always used before subject in passive voice. Sometimes
words “with, to, etc” may also be used before subject in passive voice.
Examples.
Active voice: The water fills the tub.
Passive voice: The tub is filled with water.
Active voice: He knows me.
Passive voice: I am known to him. - Auxiliary
verbs are used passive voice according to the tense of sentence.
PASSIVE VOICE FOR ALL TENSES RULES
- The
places of subject and object in sentence are inter-changed in passive
voice. - 3rd
form of verb (past participle) will be used only (as main verb) in passive
voice. - Auxiliary
verbs for each tense are given below in the table.
|
Present
Simple Tense (passive Voice) Auxiliary verb in passive voice: am/is/are |
|
|
Active voice: He sings a song. He does not sing a song.Does he sing a song? |
Passive voice: A song is sung by him. A song is not sung by him. Is a song sung by him? |
|
Present
Continuous Tense (passive Voice) Auxiliary verb in passive voice: am being/is being/are being |
|
|
Active voice: I am writing a letter I am not writing a letter. Am I writing a letter? |
Passive voice: A letter is being written by me. A letter is not being written by me. Is a letter being written by me? |
|
Present
Perfect Tense (passive Voice) Auxiliary verb in passive voice: has been/have been |
|
|
Active voice: She has finished his work She has not finished her work. Has she finished her work? |
Passive voice: Her work has been finished by her. Her work has not been finished by her. Has her work been finished by her? |
|
Past
Simple Tense (passive Voice) Auxiliary verb in passive voice: was/were |
|
|
Active voice: I killed a snake I did not kill a snake. Did I kill a snake? |
Passive voice: A snake was killed by me. A snake was not killed by me. Was a snake killed by me? |
|
Past
Continuous Tense (Passive Voice) Auxiliary verb in passive voice: was being/were being |
|
|
Active voice: He was driving a car. He was not driving a car. Was he driving a car? |
Passive voice: A car was being driven by him. A car was not being driven by him. Was a car being driven by him? |
|
Past
Perfect Tense (Passive Voice) Auxiliary verb in passive voice: had been |
|
|
Active voice: They had completed the assignment. They had not completed the assignment. Had they completed the assignment? |
Passive voice: The assignment had been completed by them. The assignment had not been complete by them. Had the assignment been completed by them? |
|
Future
Simple Tense (Passive Voice) Auxiliary verb in passive voice: will be |
|
|
Active voice: She will buy a car. She will not buy a car. Will she buy a car? |
Passive voice: A car will be bought by her. A car will not be bought by her. Will a car be bought by her? |
|
Future
Perfect Tense (passive Voice) Auxiliary verb in passive voice: will have been |
|
|
Active voice: You will have started the job. You will have not started the job. Will you have started the job? |
Passive voice: The job will have been started by you. The job will not have been started by you. Will the job have been started by you? |
Note: The following tenses cannot be changed into passive
voice.
- Present
perfect continuous tense - Past
perfect continuous tense - Future
continuous tense - Future
perfect continuous tense - Sentence
having Intransitive verbs
Passive voice for Present/Future Modals
“CAN, MAY, MIGHT,
SHOULD, MUST, OUGHT TO”
- The
places of subject and object in sentence are inter-changed in passive
voice. - 3rd
form of verb (past participle) will be used only (as main verb) in passive
voice. - To
change sentences having present/future modal into passive voice, auxiliary
verb “be” is added after modal in sentence.
|
||
|
Active voice: CAN She can play a violin. She cannot play a violin. Can she play a violin? |
|
|
|
Active voice: MAY I may buy the computer. I may not buy the computer. May I buy the computer? |
Active voice: MAY BE The computer may be bought by me. The computer may not be bought by me. May the computer be bought by me? |
|
|
Active voice: MIGHT Guests might play chess. Guests might not play chess. |
Active voice: MIGHT BE Chess might be played by guests. Chess might not be played guests. |
|
|
Active voice: SHOULD Students should study all lessons. Students should not study all lessons. Should students study all lessons? |
Active voice: SHOULD BE All lessons should be studied by students. All lessons should not be studied by students. Should all lessons be studied by students? |
|
|
Active voice: MUST You must learn the test-taking strategies. You must not learn the test-taking strategies. |
Active voice: MUST BE Test-taking strategies must be learnt by you. Test-taking strategies must not be learned by you. |
|
|
Active voice: OUGHT TO They ought to take the examination. |
Active voice: OUGHT TO BE The examination ought to be taken by them. |
|
Passive voice for Past Modals
“MAY HAVE, MIGHT HAVE,
SHOULD HAVE, MUST HAVE, OUGHT TO HAVE”
- The
places of subject and object in sentence are inter-changed in passive
voice. - 3rd
form of verb (past participle) will be used only (as main verb) in passive
voice. - To
change sentences having past modal into passive voice, auxiliary verb
“been” is added after modal in sentence.
|
||
|
Active voice: MAY HAVE You may have availed the opportunity. You may not have availed the opportunity. |
|
|
|
Active voice: MIGHT HAVE He might have eaten meal. He might not have eaten meal. |
Active voice: MIGHT HAVE BEEN Meal might have been eaten by him. Meal might not have been eaten by him. |
|
|
Active voice: SHOULD HAVE You should have studied the book. You should not have studied the book. |
Active voice: SHOULD HAVE BEEN The book should have been studied by you. The book should have not been studied by you. |
|
|
Active voice: MUST HAVE He must have started job. He must not have started job. |
Active voice: MUST HAVE BEEN Job must have been started by you. Job must not have been started by you. |
|
|
Active voice: OUGHT TO HAVE You ought to have helped him. |
Active voice: OUGHT TO HAVE BEEN He ought to have been helped by you |
|
Passive voice of imperative sentences
(command and request)
A sentence
which expresses command or request or advice is called imperative sentence.
For example,
Open the door.
Turn off the television.
Learn your lesson.
For changing these sentences in to passive voice, auxiliary verb “be” is used.
The word “Let” is added before sentence in passive voice. Auxiliary verb “be”
is added after object in sentence in passive voice. Main verb (base form) of
imperative sentence is changed to 3rd form of verb (past participle) in passive
voice. For best understand read the following examples.
Examples
Passive
|
|
Active
|
Passive
|
|
Open the door. |
Let the door be opened. |
|
Complete the work. |
Let the worked be completed. |
|
Turn off the television. |
Let the television be tuned off. |
|
Learn your lesson. |
Let your lesson be learnt. |
|
Kill the snake. |
Let the snake be killed. |
|
Punish him. |
Let him be punished. |
|
Speak the truth. |
Let the truth be spoken. |
|
Help the poor. |
Let the poor be helped. |
|
Revise your book. |
Let your book be revised. |
|
Clean your room.
|
Let
your room be cleaned. |
Sentences which cannot be changed into passive voice
Transitive and intransitive verb
A verb can
be either transitive or intransitive. A transitive verb needs an object (in
sentence) to give complete meaning while intransitive verb does need an object
(in sentence) to give complete meaning.
For example,
Transitive verb.
He sent a letter.
(Send is a transitive verb and it needs an object i.e. letter to express
full meaning.)
Intransitive Verb.
He laughs.
(Laugh is an intransitive verb and it does not
need object for expressing full meaning.)
e.g. Sleep, go, reach, sit, die, are examples of
intransitive verbs.
Intransitive verb cannot be changed into passive voice
The
sentences having intransitive verbs (belonging to any tense) cannot be changed
into passive voice. The reason is that there is not any object in such
sentences and without object of sentence passive voice is not possible.
A sentence can be changed into passive voice if it has subject and object.
Sometimes subject may not be written in passive voice but it does not mean that
it has no subject. Such sentences have subject but the subject is so common or
familiar or known that if even it is not written in passive voice, it gives
full meaning.
For example
Cloth is sold in
yards.
The
following tenses can also not be changed into passive voice.
- Present
perfect continuous tense - Past
perfect continuous tense - Future
continuous tense - Future
perfect continuous tense