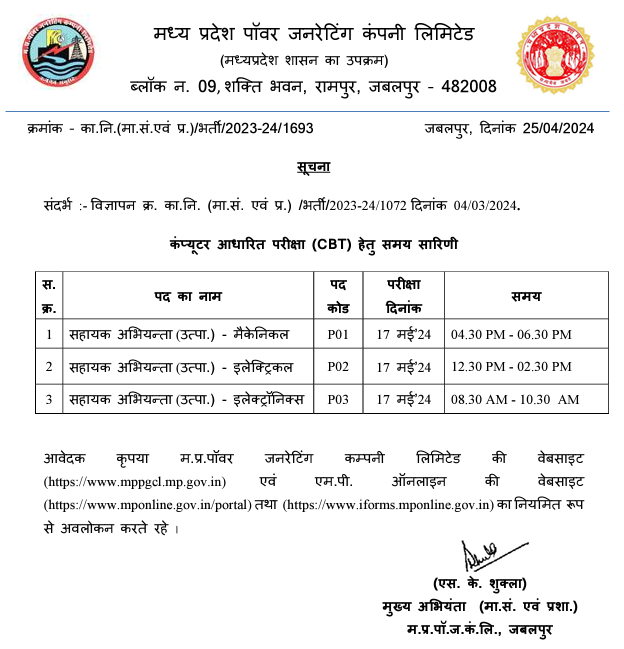
Power Systems Transmissions Part 4

Category –EE Online Test
Telegram-Join Us On Telegram
Attempt Free Power Systems Transmissions Part 4 Here. Read The Important Electrical MCQ From Below.
1) What is the general ratio of the cross sectional area of the two metals used in the A.C.S.R conductors?
a. 1 : 8
b. 1 : 4
c. 4 : 3
d. 2 : 1
ANSWER: 1 : 4
2) Assertion
(A): The maximum operating temperature of overhead line conductors made of aluminium or copper is restricted to 75 °C.
Reason (R): conductors beyond this limit may shatter the insulator.
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b. Both A and R are true and R is not the explanation of A
c. A is true but R is false
d. A is false but R is true.
ANSWER: A is true but R is false
3) For high voltage transmission lines, why are conductors suspended from towers?
a. Increase the clearance from ground.
b. Reduce clearance from ground.
c. Take care of increase in length.
d. Reduce the environmental effects.
ANSWER: Increase the clearance from ground.
Power Systems Transmissions Part 4
4) In India, which types of poles are commonly used for distribution?
a. Wooden poles
b. RCC poles
c. Steel poles
d. Both (b) and (c)
e. None of these
ANSWER: Both (b) and (c)
5) Which among these are the properties for the line supports?
a. Higher mechanical strength
b. Light in weight
c. Easy accessibility of conductors for maintenance
d. All of these
ANSWER: All of these
6) What is the maximum permissible limit of voltage for the line supports?
a. 30 kV
b. 20 kV
c. 11 kV
d. 44 kV
ANSWER: 20
7) To prevent rotting oil the wooden poles which oil is impregnated to it?
a. Kerosene oil
b. Mineral oil
c. Creosote oil
d. All of these
ANSWER: Creosote oil
Power Systems Transmissions Part 4
8) Steel poles are painted so as to prevent it from ____________.
a. Corrosion
b. Borer
c. Termites
d. All of these
ANSWER: Corrosion
9) Which among these is not a type of steel poles?
a. Rail poles
b. Tubular poles
c. Rolled steel joints
d. None of these
ANSWER: None of these
10) What is the usual span of the RCC poles?
a. 250 – 400 m.
b. 80 – 150 m.
c. 50 – 105 m.
d. 10 – 75 m.
ANSWER: 80 – 150 m
Power Systems Transmissions Part 4
11) What is the main purpose for guy wire?
a. Supports the pole
b. Protects against the surges
c. Provides emergency earth route
d. All of these
ANSWER: Supports the pole
12) Sag depends on which factor?
a. Span length
b. Weight of the conductors
c. Tension in the conductors
d. All of these
ANSWER: All of these
13) What is the shape that is attained by the conductors if suspended from the same height?
a. Parabola
b. Catenary
c. Semi circle
d. None of these
ANSWER: Catenary
14) Conductor sag should be kept
a. Minimum
b. Maximum
c. Zero
d. None of these
ANSWER: Minimum
Power Systems Transmissions Part 4
15) What is the minimum safety factor in respect of the conductor tension?
a. 1
b. 3
c. 2
d. 1.5
ANSWER: 2
16) A 132 kV transmission line, with the weight of conductor = 680 kg/km, length of span = 260 m, ultimate strength = 3100 kg, safety factor =2. Calculate the height above ground at which the conductor should be supported.
Ground clearance required is 10 m
a. 10.7 m
b. 13.7 m
c. 20.83 m
d. 18.75 m
ANSWER: 13.7 m
17) Sag is directly proportional to the square of span.
a. True
b. False
ANSWER: True
18) The maximum tension in a section of overhead line conductor between two supports of unequal height occurs at
a. The higher support
b. The lower support
c. Midpoint of the conductors
d. None of these
ANSWER: The higher suppor
Power Systems Transmissions Part 4
19) Safety factor is the ratio of
a. Working stress to breaking stress.
b. Breaking stress to working stress.
c. 1 / breaking stress.
d. 1 / working stress.
ANSWER: Breaking stress to working stress.
20) What is the effect of temperature rise on the over head lines?
a. Increase the sag and decrease the tension
b. Decrease the sag and increase the tension
c. Both increases
d. Both decreases
ANSWER: Increase the sag and decrease the tension
21) A transmission line has a span of 250 metres between the line supports. The conductors has a cross sectional area of 1.29 cm2 and weighs 1170 kg/km and has a breaking stress of 4218 kg/cm2. Calculate the sag and vertical sag with a safety factor of 5, with a wind pressure of 122 kg per square metre of the projected area.
a. 14 and 5.37
b. 16 and 8.39
c. 14 and 8.39
d. 15 and 5.37
ANSWER: 14 and 8.39
22) Why is stringing chart useful?
a. For finding the sag in the conductor
b. In the design of insulator string
c. In the design of tower
d. To find the distance between the towers
ANSWER: For finding the sag in the conductor
Power Systems Transmissions Part 4
23) Which line represents the tension in the given graph?
a. I
b. II
c. III
d. IV
ANSWER: II
24) In the following graph which curve represents the sag?
a. I
b. II
c. III
d. IV
ANSWER: I
25) Hot template curves are a plot between
a. Temperature and humidity
b. Conductors sag and span lengths
c. Conductor weight and sag
d. None of these
ANSWER: Conductors sag and span lengths
26) Galloping in transmission line conductors arises due to
a. Asymmetrical layers of ice formation.
b. Vortex phenomenon in light winds.
c. Heavy weight of the line conductors.
d. Adoption of horizontal conductor configuration.
ANSWER: Asymmetrical layers of ice formation.
Power Systems Transmissions Part 4
27) What is the frequency of aeoline vibrations?
a. fα = 2 * (Vp / d) * 1000
b. fα = 2 * (Vp * d) * 1000
c. fα = 2 / (Vp * d) * 1000
d. fα = 2 / (Vp / d) * 1000
ANSWER: fα = 2 * (Vp / d) * 1000
28) What are the different types of vibrations in the vertical plane?
a. Aeoline vibrations
b. Galloping
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of these
ANSWER: Both (a) and (b)
29) What is the minimum clearance of HV lines from ground across the streets?
a. 3 m.
b. 6 m.
c. 5 m.
d. 8 m.
ANSWER: 6 m.
Power Systems Transmissions Part 4
30) What is the minimum horizontal clearance of a LV line from a residential building?
a. 0.6 m.
b. 0.9 m.
c. 1.2 m.
d. 1.6 m.
ANSWER: 1.2 m.
31) If a 132 kV line passes over a residential building, what shall be the minimum vertical clearance from the roof of the building?
a. 3 m.
b. 4.57 m.
c. 6.38 m.
d. 9.27 m.
ANSWER: 4.57 m.
32) What is the minimum clearance provided for the 132 kV line from the ground?
a. 3.2 m.
b. 6.4 m.
c. 7.5 m.
d. 10.5 m.
ANSWER: 6.4 m.
Power Systems Transmissions Part 4
33) What is the horizontal spacing between phase conductors of 132 kV line?
a. 8 m.
b. 11 m.
c. 14 m.
d. 17 m.
ANSWER: 8 m.
34) Which type of insulator is used on 132 kV transmission lines?
a. Pin type
b. Disc type
c. Shackle type
d. Pin and shackle type
ANSWER: Disc type
35) Where are the strain type insulators used?
a. At dead ends
b. At any intermediate anchor tower
c. On straight runs
d. Either (a) or (b)
ANSWER: Either (a) or (b)
36) Porcelain is produced by firing at high temperature due to mixtures of _________.
a. Kaolin
b. Feldspar
c. Quartz
d. All of these
ANSWER: All of these
Power Systems Transmissions Part 4
37) What is the dielectric strength of porcelain?
a. 55 kV/cm.
b. 60 kV/cm.
c. 75 kV/cm.
d. 80 kV/cm.
ANSWER: 60 kV/cm.
38) Why is the wavy structure of pin insulators used?
a. Increases mechanical strength.
b. Increases puncture strength.
c. Increases flash over voltage.
d. Increases thermal strength.
ANSWER: Increases flash over voltage.
Power Systems Transmissions Part 4
39) The number of discs in a string of insulators for 400 kV ac over head transmission line lies in the range of
a. 32 – 33
b. 22 – 23
c. 15 – 16
d. 9 – 10
ANSWER: 22 – 23
40) What is the maximum voltage level upto which the pin type insulators can be used?
a. 22 kV
b. 33 kV
c. 66 kV
d. 132 kV
ANSWER: 33 kV
Power Systems Transmissions Part 4