|
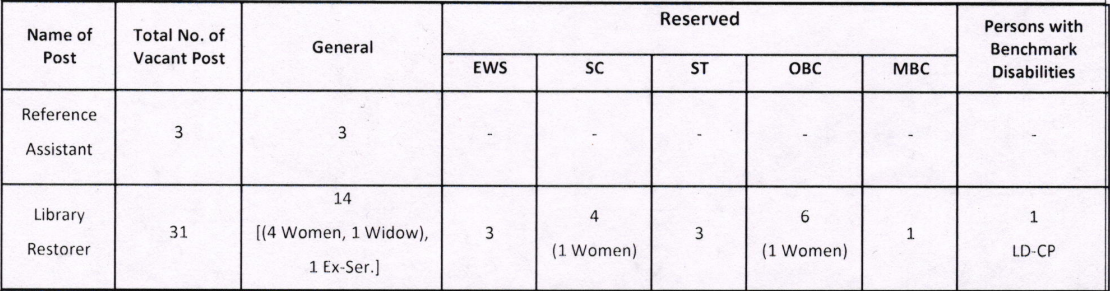
Unit
|
Symbol
|
General Quantities
|
|
m/s2 (metre/second/second)
|
a
|
Acceleration, linear
|
|
m2 (square metre)
|
A
|
Area
|
|
J (joule)
|
W
|
Energy or work
|
|
N (newton)
|
F
|
Force
|
|
m (meter)
|
l
|
Length
|
|
kg (kilogram)
|
m
|
Mass
|
|
W (watt)
|
P
|
Power
|
|
Pa (pascal)
|
p
|
Pressure
|
|
K or °C (Kelvin or degree Celsius)
|
θ
|
Temperature value
|
|
s (second)
|
t
|
Time
|
|
Nm (newton metre)
|
T
|
Torque
|
|
rad/s (radian/second)
|
ω
|
Velocity, angular
|
|
m/s (metre/second)
|
v or u
|
Velocity, linear
|
|
m3 (cubic metre)
|
V
|
Volume
|
|
m meter
|
λ
|
Wavelength
|
|
Unit
|
Symbol
|
Electrical Quantities
|
|
Ω(ohm)
|
Y
|
Admittance
|
|
C (coulomb)
|
Q
|
Charge (quantity)
|
|
S (siemen)
|
G
|
Conductance
|
|
A (ampere)
|
I
|
Current
|
|
A/m2 (ampere/square
metre) |
J
|
Current density
|
|
V (volts)
|
E
|
Electromotive force (emf)
|
|
Hz (hertz)
|
f
|
Frequency
|
|
Ω (ohm)
|
Z
|
Impedance
|
|
s (second)
|
T
|
Period
|
|
V (volt)
|
V
|
Potential difference (p.d.)
|
|
W (watt)
|
P
|
Power, active
|
|
VA (volt ampere)
|
S
|
Power, apparent
|
|
VAr (volt ampere reactive)
|
Q
|
Power, reactive
|
|
Ω (ohm)
|
X
|
Reactance
|
|
Ω (ohm)
|
R
|
Resistance
|
|
Ωm (ohm metre)
|
ρ
|
Resistivity
|
|
s (second)
|
t
|
Time constant
|
|
Unit
|
Symbol
|
Electrostatic Quantities
|
|
F (farad)
|
C
|
Capacitance
|
|
V/m (volt/metre)
|
E
|
Field strength
|
|
C (coulomb)
|
Ψ
|
Flux
|
|
C/m2 (coulomb/square
metre) |
D
|
Flux density
|
|
F/m (farad/metre)
|
ε
|
Permittivity, absolute
|
|
Unit
|
Symbol
|
General
Quantities |
|
no units
|
εr
|
Permittivity,
relative |
|
F/m
(farad/metre) |
ε0
|
Field strength
|
|
Unit
|
Symbol
|
Electromagnetic Quantities
|
|
At/m (ampere turn/metre)
|
H
|
Field strength
|
|
Wb (weber)
|
Φ
|
Flux
|
|
T (tesla)
|
B
|
Flux density
|
|
H (henry)
|
M
|
Inductance, mutual
|
|
H (henry)
|
L
|
Inductance, self
|
|
At (ampere-turn)
|
F
|
Magnetomotive force (mmf)
|
|
H/m (henry/metre)
|
μ
|
Permeability, absolute
|
|
no units
|
μr
|
Permeability, relative
|
|
H/m (henry/metre)
|
μ0
|
Permeability, of free space
|
|
At/Wb (ampere turn/weber) Siemens
|
S
|
Reluctance
|