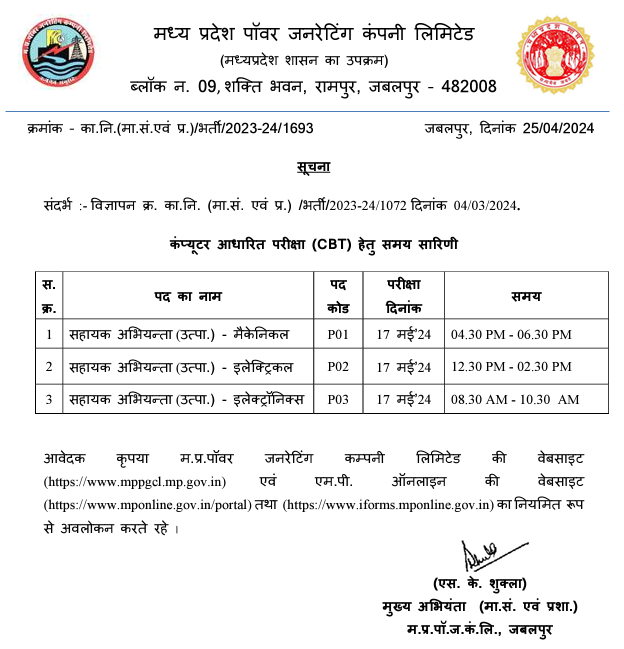
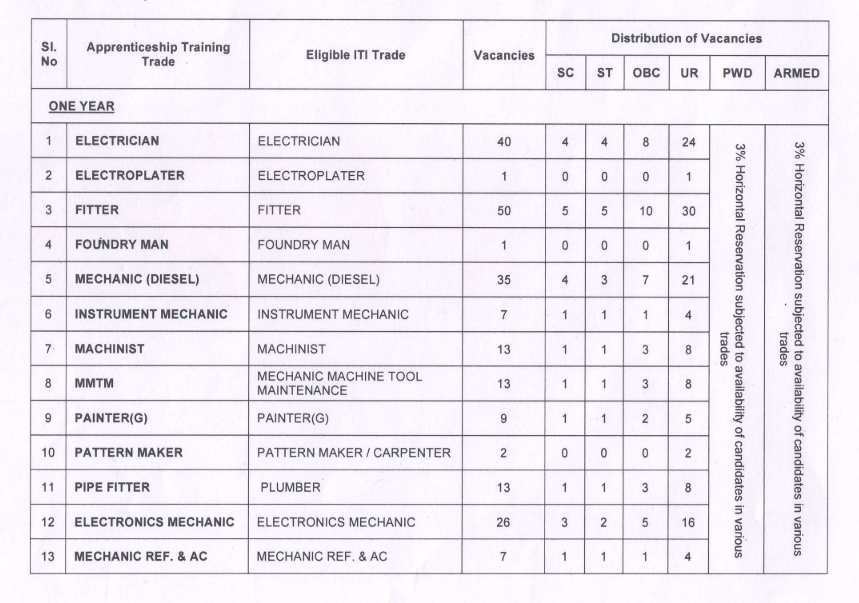
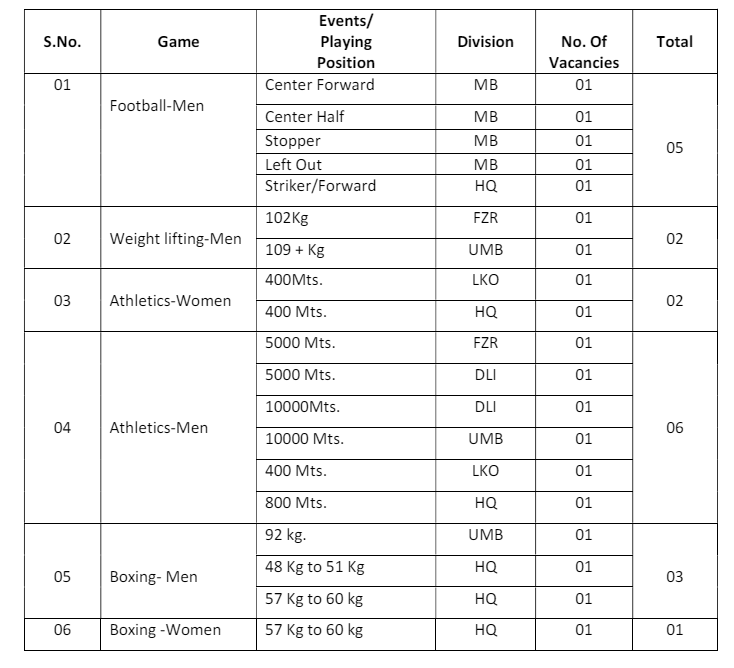
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8

Category –EE Online Test
Telegram-Join Us On Telegram
Attempt Free Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8 Here. Read The Important Electrical MCQ From Below.
1) In a salient pole synchronous generator direct axis reactance is
a. Greater than quadrature axis reactance
b. Less than quadrature axis reactance
c. Equal to quadrature axis reactance
d. None of the above
ANSWER: Greater than quadrature axis reactance
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8
2) The reluctance power of a salient pole alternator is given by
a. V2[Xd – Xq / 2XdXq] sin2 δ
b. V2[Xq – Xd / 2Xd Xq] sin2 δ
c. V2[Xd – Xq / XdXq] sin δ
d. V[Xd – Xq / 2Xd Xq] sin2 δ
ANSWER: V2[Xd – Xq / 2XdXq] sin2 δ
3) In case of salient pole alternators, maximum output power can be obtained when power angle (d) is
a. Less than 90 degree
b. Equal to 90 degree
c. Greater than 90 degree
d. None of the above
ANSWER: Less than 90 degree
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8
4) Two identical alternators having impedances Z1 and Z2 are connected in parallel produces E1 and E2 as their induced emf’s. if no load is connected to the alternators then a circulating current will flow in the circuit. This current is given by
a. E1 + E2 / Z1 – Z2
b. E1 – E2 / Z1 + Z2
c. E2 – E1 / Z1 + Z2
d. E1 + E2 / Z1 + Z2
ANSWER: E1 – E2 / Z1 + Z2
5) If a 3 phase alternator is short circuited at its terminal, then the initial value of short circuit current will be limited by
a. Synchronous reactance
b. Transient reactance
c. Sub transient reactance
d. All of the above
ANSWER: Sub transient reactance
6) The change in excitation of the two alternators operating in parallel causes
a. Only the kVAR sharing of two alternators without disturbing kW sharing of the two machines
b. Only the kW sharing of two alternators without disturbing kVAR sharing of the two machines
c. Both the kVAR sharing and kW sharing of two alternators
d. None of the above
ANSWER: Only the kVAR sharing of two alternators without disturbing kW sharing of the two machines
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8
7) In case of hydro generators, the driving torque can be changed by controlling the
a. Gate opening
b. Throttle opening
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of these
ANSWER: Gate opening
8) The increase in mechanical torque in case of alternator will
a. Increase the armature current and reduce the power factor
b. Increase the armature current and improve the power factor
c. Decrease the armature current and improve the power factor
d. Decrease the armature current and reduce the power factor
ANSWER: Increase the armature current and improve the power factor
9) When an alternator is connected to infinite bus bar, change in excitation for alternator will
a. Change the terminal voltage and power factor both
b. Affect only terminal voltage and power factor remains unaffected
c. Affect only power factor and terminal voltage remains unaffected
d. Neither terminal voltage will get affected nor power factor
ANSWER: Affect only power factor and terminal voltage remains unaffected
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8
10) The plot of armature current verses excitation is known as V curves for synchronous generator. Determine the correct combination of load.
a. A – full load, B – half load, C – no load
b. A – full load, B – no load, C – half load
c. A – no load, B – half load, C – full load
d. A – half load, B – full load, C – no load
ANSWER: A – full load, B – half load, C – no load
11) If a three phase winding is displaced in space by 120 degree in a synchronous motor then the magnitude of resultant flux when it is rotated by Θ = 0 degree and Θ = 60 degree is
a. 0, 1.5 times the magnitude of maximum flux
b. 1.5 times the magnitude of maximum flux, 0
c. 0.866 times the magnitude of maximum flux, 1.5 times the magnitude of maximum flux
d. 1.5 times the magnitude of maximum flux, 1.5 times the magnitude of maximum flux
ANSWER: 1.5 times the magnitude of maximum flux, 1.5 times the magnitude of maximum flux
12) For a half cycle of fluxes in a synchronous motor, the resultant flux has rotated through
a. 0 degree
b. 90 degree
c. 180 degree
d. 360 degree
ANSWER: 180 degree
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8
13) For a two pole, 50 Hz, 3 phase synchronous motor the speed of rotating magnetic field is
a. 1000 rpm
b. 2000 rpm
c. 3000 rpm
d. 3500 rpm
ANSWER: 3000 rpm
14) A synchronous motor draws 2 MVA at a power factor of 0.8 leading. If the efficiency developed in the motor is 90% then the power developed is equal to
a. 1212 kW
b. 1440 kW
c. 1676 kW
d. 1767 kW
ANSWER: 1440 kW
15) Synchronous motor works on the principle of
a. Mutual induction
b. Electromagnetic induction
c. Magnetic locking
d. None of these
ANSWER: Magnetic locking
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8
16) Synchronous motors are
a. Self starting
b. Not self starting
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of these
ANSWER: Not self starting
17) Can synchronous motor rotate at any speed other than the synchronous speed?
a. Yes
b. No
ANSWER: No
18) The method used for starting synchronous motor is/are
a. Using pony motors
b. Using damper windings
c. As a slip ring induction motor
d. All of the above
ANSWER: All of the above
19) A synchronous motor is started by using damper winding. When the motor runs at synchronous speed then the induced emf in the damper winding will be
a. Zero
b. Maximum
c. Half of the terminal voltage
d. None of these
ANSWER: Zero
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8
20) With increase in load, the speed of synchronous motor
a. Increases
b. Decreases
c. Remains constant
d. None of the above
ANSWER: Remains constant
21) Back emf in case of synchronous motor depends on the
a. Excitation given to the field winding
b. Speed
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of the above
ANSWER: Excitation given to the field winding
22) If the load on a synchronous motor increases then its
a. Current drawn by motor increases and load angle decreases
b. Current drawn by motor decreases and load angle remains constant
c. Current drawn by motor remains constant and load angle increases
d. Current drawn by motor increases and load angle also increases
ANSWER: Current drawn by motor increases and load angle also increases
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8
23) In a synchronous motor the torque produced will be maximum when load angle is equal to
a. 0° electrical
b. 90° electrical
c. 180° electrical
d. 360° electrical
ANSWER: 90° electrical
24) Practically in a synchronous motor, the pull-out torque will occur when the torque angle is nearly equal to
a. 30° electrical
b. 45 ° electrical
c. 60 ° electrical
d. 75 ° electrical
ANSWER: 75 ° electrical
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8
25) For a synchronous motor, as the load angle reaches up to 90 ° electrical i.e. half a pole pitch, then the magnetic locking between the stator and rotor
a. No longer exist
b. Will be strongest
c. Will be weakest
d. None of these
ANSWER: No longer exist
26) The impedance angle or internal machine angle (°) of a synchronous motor is equal to
a. tan-1Xs / Ra
b. tan-1 Rs / Xa
c. tan-1 Xs / Za
d. tan-1 Zs / Ra
ANSWER: tan-1Xs / Ra
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8
27) When the excitation of a synchronous motor is changed keeping the load constant then the
a. Power factor will change
b. Ia cos ∅ remains constant
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of these
ANSWER: Both (a) and (b)
28) Under excitation occurs when the magnitude of induced emf of synchronous motor is less than the applied voltage. During under excitation the current drawn by the motor and power factor
a. Increases, decreases and will be lagging in nature
b. Decreases, increases and will be leading in nature
c. Increases, increases and will be leading in nature
d. Decreases, decreases and will be lagging in nature
ANSWER: Increases, decreases and will be lagging in nature
29) If the field of the synchronous motor is overexcited then its power factor will be
a. Lagging
b. Leading
c. Unity
d. Zero
ANSWER: Leading
30) For critical excitation the power factor of the synchronous motor will be equal to
a. 0
b. 1
c. 0.5 MΩ
d. None of the above
ANSWER: 1
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8
31) If graph of armature current drawn by synchronous motor is against field current is plotted then the resulted graph is known as
a. V-curves
b. Inverted V-curves
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of these
ANSWER: V-curves
32) The plot of power factor against the field current of synchronous motor is known as
a. V-curves
b. Inverted V-curves
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of these
ANSWER: Inverted V-curves
33) The expression for the mechanical power developed in terms of the load angle δ and the internal machine angle ∅, for constant voltageVph and constant excitation Eb is
a. [{(EbVph) / Zs} * cos(θ – δ)] – [{(E2b) / Zs} * cos θ]
b. [{(EbV ph) / Zs} * cos(δ – θ)] – [{(E2b) / Zs}* cos θ]
c. [{(E2b) / Zs} * cos θ] – [{(Eb Vph) / Zs} * cos(δ – θ)]
d. [{(E2b) / Zs} * cos θ] – [({Eb Vph) / Zs} * cos(θ – δ)]
ANSWER: [{(EbVph) / Zs} * cos(θ – δ)] – [{(E2b) / Zs} * cos θ]
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8
34) The value of load angle δ and the internal machine angle ∅ for maximum power developed in synchronous motor is equal to
a. 0°electrical, 0° electrical
b. 0° electrical, 90° electrical
c. 90° electrical, 0° electrical
d. 90° electrical, 90° electrical
ANSWER: 90° electrical, 90° electrical
35) A synchronous motor is running at a load angle of 25 degree at rated frequency with negligible armature resistance. Now, if the supply frequency is increased by 15% keeping the other parameters constant, then the new load angle will be equal to
a. 26.89 degree
b. 29.07 degree
c. 32.05 degree
d. 38.20 degree
ANSWER: 29.07 degree
36) Oscillations of the rotor about its new equilibrium position, due to sudden application or removal of load in synchronous motor is called
a. Hunting
b. Galloping
c. Swinging
d. Both (a) and (c)
e. None of the above
ANSWER: Both (a) and (c)
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8
37) Hunting in a synchronous motor results in
a. Loss of synchronism
b. Mechanical and electrical stresses on motor
c. Large current drawn by motor
d. all of the above
e. None of the above
ANSWER: all of the above
38) In a synchronous motor, the phenomenon of hunting caused by the sudden application or removal of load is prevented by
a. Using damper winding
b. Using a capacitor
c. Using an inductor
d. All of the above
e. None of the above
ANSWER: Using damper winding
Electrical Machines Expected MCQ PDF 8